Introduction
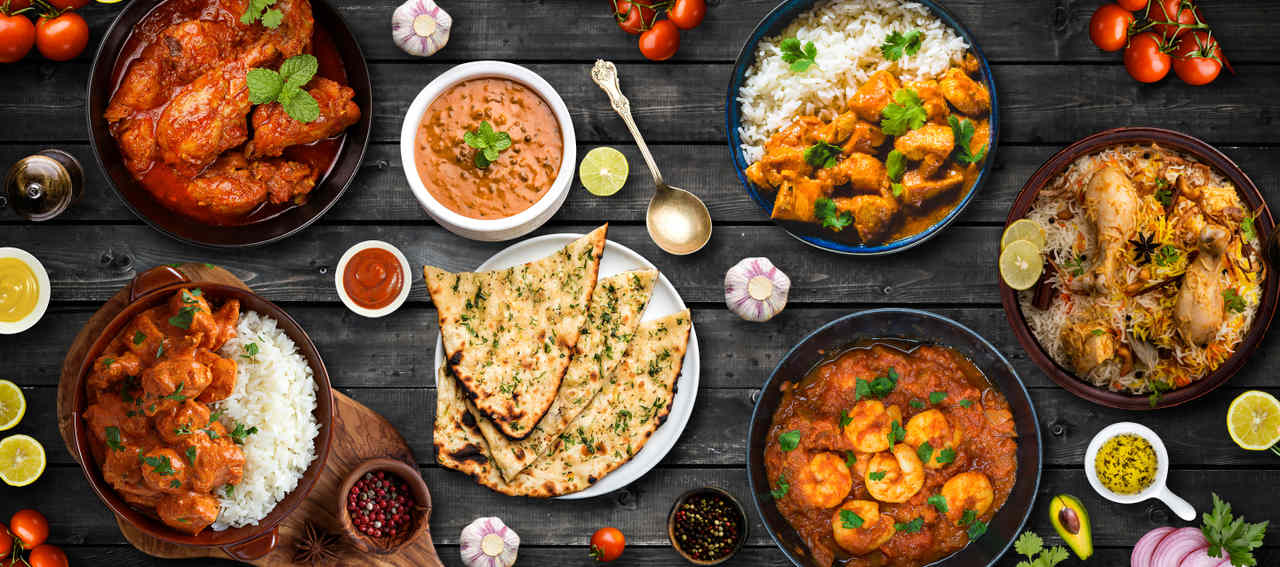
Indian restaurants have become an integral part of culinary landscapes across the globe, offering a rich tapestry of flavours, aromas, and experiences. The significance of these establishments extends beyond mere dining; they serve as cultural ambassadors, showcasing the diversity of Indian cuisine and traditions. As international appreciation for Indian food continues to grow, understanding the role of Indian restaurants in local communities becomes increasingly relevant.
Diverse Offerings and Culinary Techniques
Indian restaurants range from casual dining spots to upscale establishments, providing patrons with a variety of culinary experiences. Signature dishes like biryani, butter chicken, and dosa reflect the intricate blend of spices and cooking techniques inherent in Indian cuisine. Moreover, restaurants often showcase regional flavours, from the rich curries of North India to the tangy, coconut-infused dishes of South India.
The rise of vegetarian and vegan options within Indian restaurants has also broadened their appeal, catering to health-conscious diners and those with dietary restrictions. Many Indian dishes are naturally plant-based, allowing restaurants to highlight these in innovative ways, making traditional meals accessible to a wider audience.
Current Trends and Challenges
In recent years, the Indian restaurant industry has faced both challenges and opportunities. The COVID-19 pandemic prompted many establishments to adapt by offering delivery and takeout services, expanding their reach to patrons staying at home. As restrictions ease, a resurgence in dine-in customers has been noted, along with an increased interest in authentic and unique culinary experiences.
Sustainability has also emerged as a key focus. Many Indian restaurants are now sourcing local ingredients, reducing waste, and adopting eco-friendly practices to appeal to the environmentally conscious consumer.
The Cultural Significance
The importance of Indian restaurants transcends food; these establishments foster community connections and offer a taste of home for Indian diaspora. They often serve as gathering places for celebrations, festivals, and culturally significant events, weaving together the fabric of local societies with the richness of Indian heritage.
Conclusion
In summary, Indian restaurants play a crucial role in promoting culinary diversity and cultural understanding. With their unique offerings and community-oriented focus, they are positioned well for continued growth and relevance in the global dining scene. As the appreciation for Indian cuisine continues to blossom, these restaurants will likely adapt and innovate, ensuring they remain vital parts of both local and global gastronomy. The future looks promising for Indian restaurants, as they continue to bridge cultures and delight taste buds worldwide.