Introduction to the Periodic Table
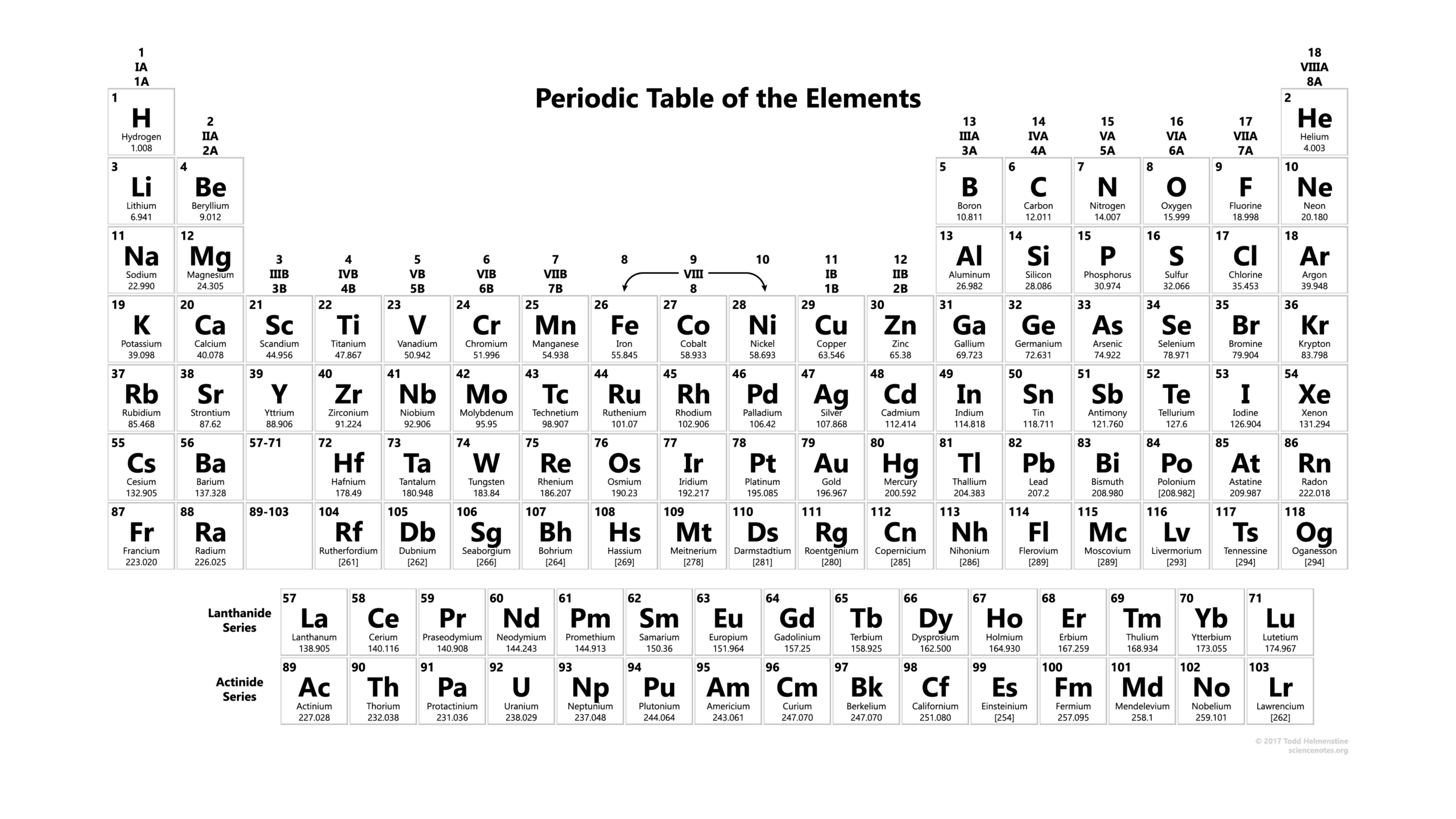
The periodic table is one of the most significant achievements in the field of chemistry. Developed in the 19th century by Dmitri Mendeleev, it provides a systematic arrangement of chemical elements based on their atomic number and properties. Its importance lies not only in its use as a reference tool for scientists but also in how it helps predict the behaviour of elements in chemical reactions. As we face global challenges, understanding the periodic table has become increasingly relevant in fields such as materials science, environmental studies, and pharmaceuticals.
Structure and Organisation
The periodic table is organised into rows called periods and columns known as groups or families. Elements in the same group display similar chemical properties due to their similar valence electron configurations. For instance, Group 1 elements, known as alkali metals, are all highly reactive, while the noble gases in Group 18 are largely inert. The table’s layout allows chemists to quickly glean information about an element’s atomic mass, electronegativity, and other characteristics.
Recent Discoveries and Updates
As of 2023, the periodic table includes 118 confirmed elements, with a few being synthetically produced in laboratories. Researchers continuously explore new materials and combinations, expanding our understanding of chemical properties and potential uses. Notably, elements such as oganesson (Og) and tennessine (Ts) highlight the ongoing pursuit of discovering heavier and more complex elements, even though these synthetic elements often have very short half-lives and limited applications.
Significance in Modern Science
The periodic table serves as a critical tool for scientists across various disciplines. In materials science, for instance, understanding metallic properties can lead to the development of more durable building materials or the creation of superconductors. In biology and medicine, knowledge of chemical elements is essential for drug development and understanding metabolic pathways. Furthermore, in the context of climate change, research into elements is vital for developing sustainable technologies, such as hydrogen fuel cells using specific metals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the periodic table is not just a list of elements; it is a foundational component of modern science that enables researchers to navigate the complexities of chemical interactions. With ongoing advancements in the understanding of chemical properties and behavior, the significance of the periodic table will only continue to grow. Researchers and educators alike encourage the study of this invaluable asset, as it holds the keys to a multitude of scientific breakthroughs that can tackle pressing global issues.