Introduction to Weather Radar Map
Weather radar maps have become essential tools in meteorology, providing critical data for predicting and monitoring weather conditions. These maps allow meteorologists and the public to understand current weather situations, anticipate severe weather events, and improve overall safety. Particularly in regions prone to storms and extreme weather, access to accurate radar information can significantly impact response times and preparedness.
What is a Weather Radar Map?
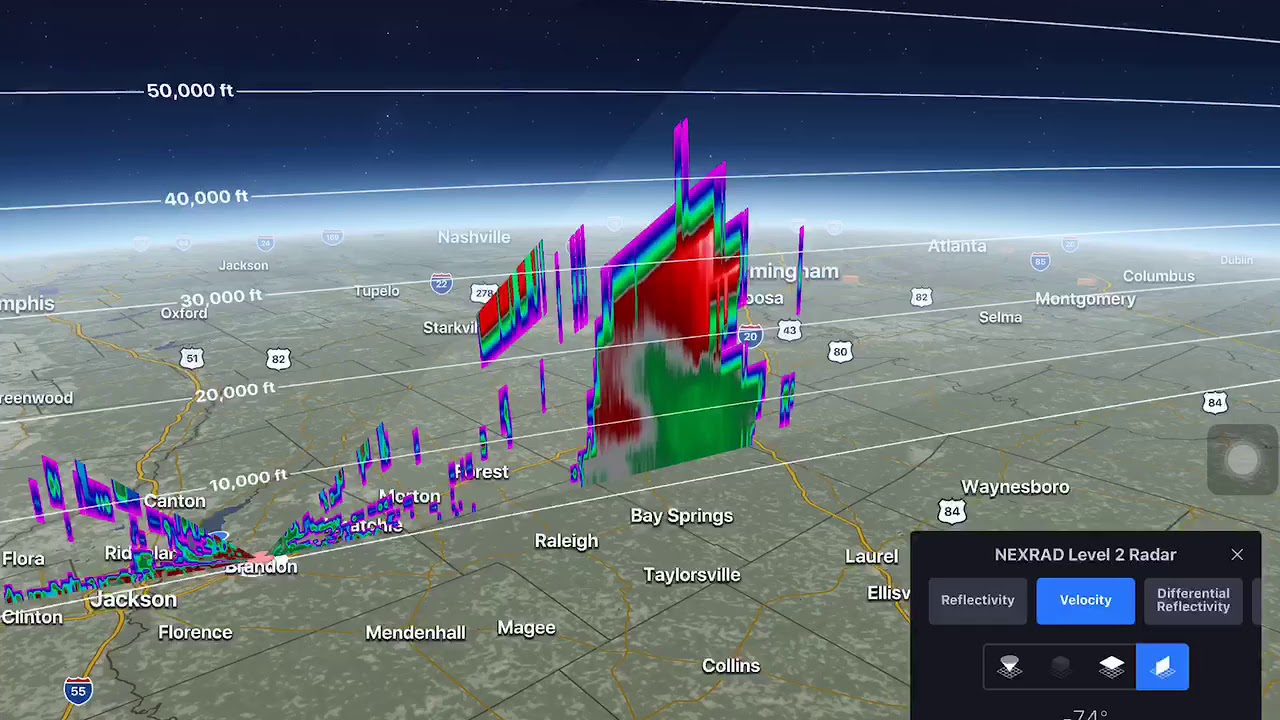
A weather radar map displays data collected by weather radar, which uses radio waves to detect precipitation, its intensity, and movement. The radar emits pulses of energy that bounce off precipitation particles, and the returning signals provide valuable information such as rainfall intensity, storm direction, and speed. This real-time data is processed and displayed on maps as comprehensive visual representations.
Recent Developments in Weather Radar Technology
Recently, advancements in weather radar technology have improved the accuracy and reliability of forecasts. For example, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has invested in dual-polarization radar technology, enhancing the ability to differentiate between rain, snow, hail, and other types of precipitation. As of March 2023, a new radar network was rolled out across the UK, providing more detailed and timely data to local meteorologists, enabling them to give more precise forecasts.
Use Cases and Benefits
Weather radar maps play a crucial role in various fields. For agriculture, they inform farmers about impending rain or drought, allowing them to manage their crops effectively. Emergency services rely on radar data to prepare for severe weather events, ensuring timely evacuations and resource allocation. Additionally, outdoor event planners use weather radar maps to monitor weather changes and make informed decisions about potential disruptions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, weather radar maps are invaluable tools that have transformed the way we understand and respond to atmospheric conditions. With continuous technological advancements, their accuracy and effectiveness are set to improve even further, making them an essential asset for meteorologists, decision-makers, and the general public. As climate change continues to affect weather patterns, the importance of reliable radar systems will only grow, reinforcing the need for investment in sophisticated meteorological technology.